What is new in Termica Neo Version 1.1.0
Build 1.1.2057.3
1. Using of Thermal Radiation
Now each container material in the material library contains the information about the emissivity coefficient. These values are used for the thermal radiation for the selected container materials. This is important at high temperatures where thermal radiation is the main mechanism of heat exchange between the surface and surrounding.

Please have a look at the example for ceramic sintering, where at the sintering temperatures 1800°C radiational heat exchange is very intensive and surface temperature is much closer to the surrounding temperature than at the room temperature.
2. Different Physical Properties for the Reacting Material and for the Product
Sometimes the physical properties of the reacting material have the big difference from the physical properties of the product. For example, during sintering of ceramics the density can increase by 40%, and thermal conductivity can increase by factor 25.
Now the physical properties of the reactant can be based on the physical properties of two materials: material before reaction, and the product after reaction. During the simulation the current physical properties change continuously from the physical properties of initial material to the physical properties of the product.
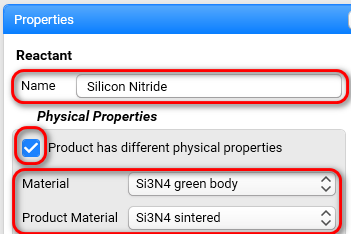
Please have a look at the example for ceramic sintering, where the green body is used as the initial material and the sintered ceramics is used as the product.
3. Actual Linear Sizes at Any Time Point
The linear changes of material during the process could be present because of two reasons:
- thermal expansion of materials because of temperature-dependent density
- different density properties for the initial material before reaction and the final product after reaction.
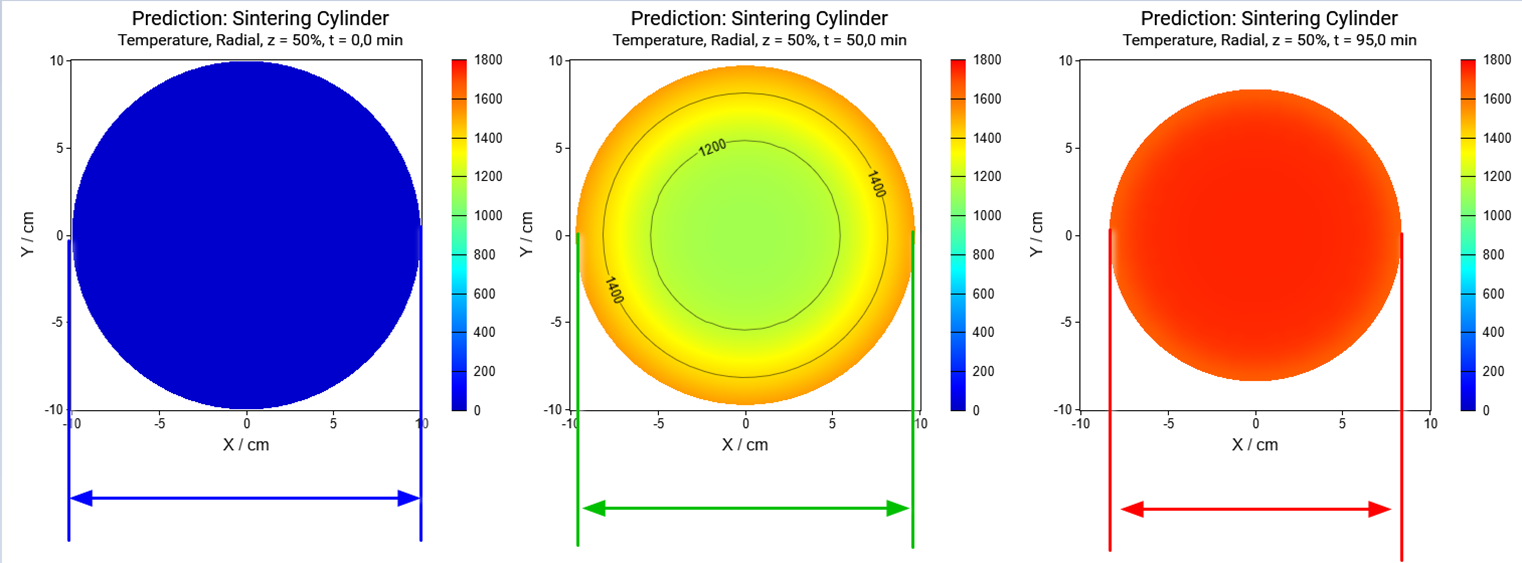
Please have a look at the example for ceramic sintering, where the linear sizes is decreased during densification by 17%, and this continuous decreasing is shown in cross-section with the time.